Ultrasound device from the future: GE VOLUSON E10
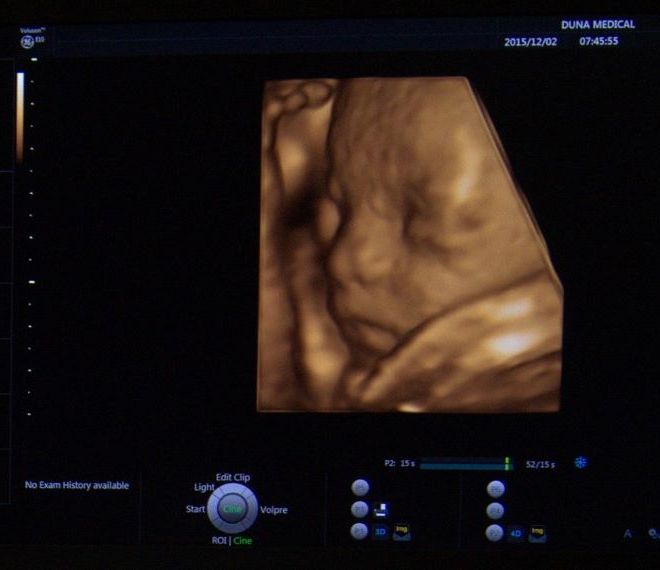
New dimensions: 3D, 4D, 5D
If we put a lot of two-dimensional (2D) images next to each other, we will have all the information to create a spatial image of the object to be examined. 3D imaging shows a static spatial image of the object to be examined; 4D means that during the examination you can see a spatial image continuously on the monitor, in the case of 5D, on a suitable monitor with glasses you can see a spatial image like in cinemas or on 3D television sets.
What the future brings: the possibility of post-processing of the images seen
With adequate computer technology capacity, wonderful prospects open up before us; in addition to the wide range of diagnostic possibilities, it is very important that – since it involves post-processing of the images – the patient is not burdened with a long examination time, even if he is dressed and sitting next to us, he can review the images together with the doctor.
4 weeks of pregnancy, visualized with the GE Voluson E10 ultrasound device
9 weeks of pregnancy displayed with the GE Voluson E10 ultrasound device
Let's list some of them:
- The images stored in the memory can be rotated in the three axes of space , so what was initially at the back, thus falling out of our field of vision, becomes clearly visible to the naked eye;
- We can cut out disturbing parts from the images (e.g. the uterine wall can be removed from the fetus);
- Since it is a three-dimensional image, individual shadows can emphasize or obscure important details; we can adjust the shadows, but we can also add lighting to the image afterwards;
- we can choose to study the surface structures , or put them in the background and direct our attention to the bones like an X-ray;
- we can make the surface parts completely "transparent", so we can also view them in space, e.g. the brain chambers of the fetus;
- Arbitrary surfaces that are curved in reality and therefore difficult to study can be spread out , e.g. the entire endometrium can be seen in one image. This is invaluable for infertility investigations, e.g. it provides great help in the accurate assessment of a polypus of the endometrium; the same method gives the opportunity to view the fetal spine from all directions after a few seconds of data collection ("scanning"), or to examine the vertebrae individually, without burdening the expectant mother with a lengthy examination. With the help of the method , we can avoid diagnostic hysteroscopy (hysteroscopy) performed under anesthesia and during hospital admission, especially if a contrast material that is clearly visible with ultrasound is injected into the uterine cavity.;
- Tomographic representation: during the examination, it is possible for the machine to make sections of the object to be examined with an arbitrarily defined thickness;
- Volume analysis: the device can recognize liquid-containing formulas and independently measure their diameters and then calculate the volume as well. We can see its great benefit during infertility treatments, when we use medication in the ovaries to help the growth of ovules (and the follicles that contain them);
- VOCAL mode: the system is able to circle a lesion (myoma, cyst) in space, calculate its volume, and then compare the increase or decrease during a repeated examination, greatly facilitating the monitoring of the effectiveness of tumor treatments;
- Elastography: the machine can separate and quantify the elasticity of individual tissues, and can compare them, so it can play a major role in recognizing and isolating small tumor tissues or endometriosis.
- Flow tests: compared to traditional flow tests (Doppler), it is possible to visualize the vascular network in space; it is much easier to recognize the placenta or a possible umbilical cord knot. The vascular network of tumors can also be mapped very precisely , thus significantly facilitating the planning of surgeries.
