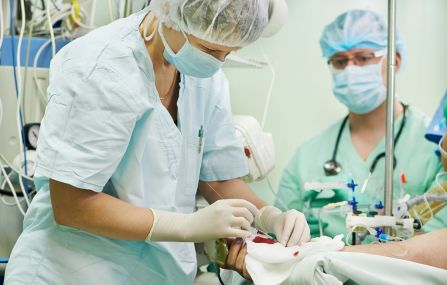
 Orthopedics is a medical specialty dealing with problems of the musculoskeletal system, while traumatology deals with changes following injuries. The treatment of orthopedic and traumatologic problems often requires surgical intervention. The surgeons at Duna Medical Center perform surgeries using the most modern procedures, which involve the least possible intervention, thus potentially shortening the recovery time.
Orthopedics is a medical specialty dealing with problems of the musculoskeletal system, while traumatology deals with changes following injuries. The treatment of orthopedic and traumatologic problems often requires surgical intervention. The surgeons at Duna Medical Center perform surgeries using the most modern procedures, which involve the least possible intervention, thus potentially shortening the recovery time.
Lumbar Disc Herniation (Discus Hernia Lumbalis)
A healthy intervertebral disc provides a flexible and strong connection between the vertebral bodies. It protects against impacts and shocks and makes the spine flexible.
As we age, the nucleus of the disc continuously loses its fluid content, thus becoming inflexible and changing its structure. The most vulnerable discs are the lower lumbar discs. However, not only aging but also genetic factors, acquired injuries, and regular overstrain can contribute to disc wear.
The fibrous rings that surround the central, gelatinous nucleus gradually lose their elasticity, then crack and tear. As a result, the central gelatinous nucleus is displaced and pushes the torn ring parts into the spinal canal. When the wall of the disc ruptures and the flexible material inside the disc bursts through the tear, a hernia (discus hernia) forms. This process is referred to as disc herniation.
If the protruding disc fragment comes into contact with the nerve root, it can cause inflammation of the nerve, followed by its dysfunction, which may manifest as numbness, pain radiating from the back to the lower extremities, muscle strength reduction, mobility limitation, in severe cases paralysis, urinary and fecal incontinence.
The goal of conservative treatment for spinal disc herniation is to reduce nerve inflammation, which includes:
- initial bed rest,
- drug treatments (anti-inflammatories, pain relievers, muscle relaxants, sedatives),
- physiotherapy, therapeutic massage.
If conservative treatments do not bring about sufficient improvement and the patient's daily activity is significantly limited, surgery is then considered.
Surgical Treatment of Disc Herniation
The goal of the surgery is to eliminate the pressure on the nerves and thus the source of the pain.
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia, with the patient lying prone. An incision is made above the affected spinal segment, and then the herniated disc is removed, freeing the nerve root from pressure and tension. The damaged disc parts are removed from the inside of the disc. A temporary drainage tube is placed in the surgical area to drain the accumulated blood - this is removed 1-2 days after the surgery.
Both newly formed and recurrent or ruptured spinal hernias are classified according to how many segments they affect:
- operations affecting 1 and 2 segments belong to the Simple Spinal Surgeries group,
- operations affecting 3 or more segments belong to the Major Spinal Surgeries group.
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
The loss of fluid from the disc and its becoming inflexible also leads to a decrease in the height of the disc. Thus, the ligaments spanning the vertebrae - the individual segments - loosen, and the constituent elements become overloaded. The body tries to counteract this instability by forming bony spurs on the edges of the vertebrae, with which the vertebrae try to connect to each other, the connecting ligament thickens, or calcified deposits form on the joints. These factors lead to a decrease in the diameter of the spinal canal, i.e., spinal stenosis, and in this narrowed spinal canal, the nerves are further compressed, put under pressure, causing chronic pain.
The goal of conservative treatment for spinal stenosis is to eliminate the compression of the nerve elements in the canal, which includes:
- initial bed rest,
- drug treatments (anti-inflammatories, pain relievers, muscle relaxants, sedatives),
- physiotherapy, therapeutic massage.
If conservative treatments do not bring about sufficient improvement and the patient's daily activity is significantly limited, surgery is then considered.
Surgical Treatment of Spinal Stenosis:
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia, with the patient lying prone. An incision is made above the affected spinal segment, and then with the aid of a microscope, the thickened ligaments causing the nerve root compression and the bony elements causing the stenosis are removed. If a herniated disc is also present, its removal is part of the procedure as well. As a result, the diameter of the spinal canal increases and the nerve roots are released from the pressure. A temporary drainage tube is placed in the surgical area to drain the accumulated blood - this is removed 1-2 days after the surgery.
In the case of spinal stenosis, surgeries are classified according to how many segments they affect:
- operations affecting 1 and 2 segments belong to the Simple Spinal Surgeries group,
- operations affecting 3 or more segments belong to the Major Spinal Surgeries group.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Tunnel syndrome is when a constriction develops alongside the nerve running in the fissure, or the "tunnel", formed by the body's muscles, ligaments, and bones, and the nerve is put under pressure. The constriction can have several causes, e.g., inflammation, overuse, injury, fracture, bone growth, developmental abnormality. The disease most often occurs in the wrist, in which case its name is carpal tunnel or carpal canal syndrome.
If conservative treatments do not yield sufficient results, surgery ensures successful restoration of the painful condition, which is performed under local anesthesia. The essence of the surgery is to cut the palmar ligament that is pressing on the nerve, thereby eliminating the pressure, and then the surgical wound is sutured with a few stitches.

-
Arthroscopic plastic surgeryFrom 1 140 000 Ft
-
Arthroscopy and cleaningFrom 535 000 Ft
-
Arthroscopy, stabilization + implantFrom 792 000 Ft
-
Bone foreign body removalFrom 723 000 Ft
-
Carpal Tunnel surgery (general anesthesia)From 496 000 Ft
-
Carpal Tunnel surgery (local anesthesia)From 360 000 Ft
-
Dupuytren’s contracture surgery – 1 rayFrom 640 000 Ft
-
Dupuytren’s contracture surgery – 2 raysFrom 940 000 Ft
-
Dupuytren’s contracture surgery – 3 raysFrom 1 140 000 Ft
-
Ganglion surgery (general anesthesia)From 486 000 Ft
-
Ganglion surgery (local anesthesia)From 340 000 Ft
-
Metal implant removal under general anesthesia - depends on the number and size of the implants to be removed.From 586 000 Ft
-
Minor surgeries for musculoskeletal and connective tissue diseasesFrom 315 000 Ft
-
OsteotomyFrom 1 251 000 Ft
-
Other surgeries for musculoskeletal and connective tissue diseasesFrom 622 000 Ft
-
Percutaneous stapling and minor muscle, tendon and joint surgeriesFrom 303 000 Ft
-
Soft tissue surgeriesFrom 390 000 Ft
-
Splint finger surgeryFrom 340 000 Ft
-
Staple wire exception (outpatient)From 64 600 Ft
-
Tibia axis correction /ventromedialization/ open mosaicFrom 879 000 Ft













